Brain Activity Can Reveal the Severity of Autistic Traits
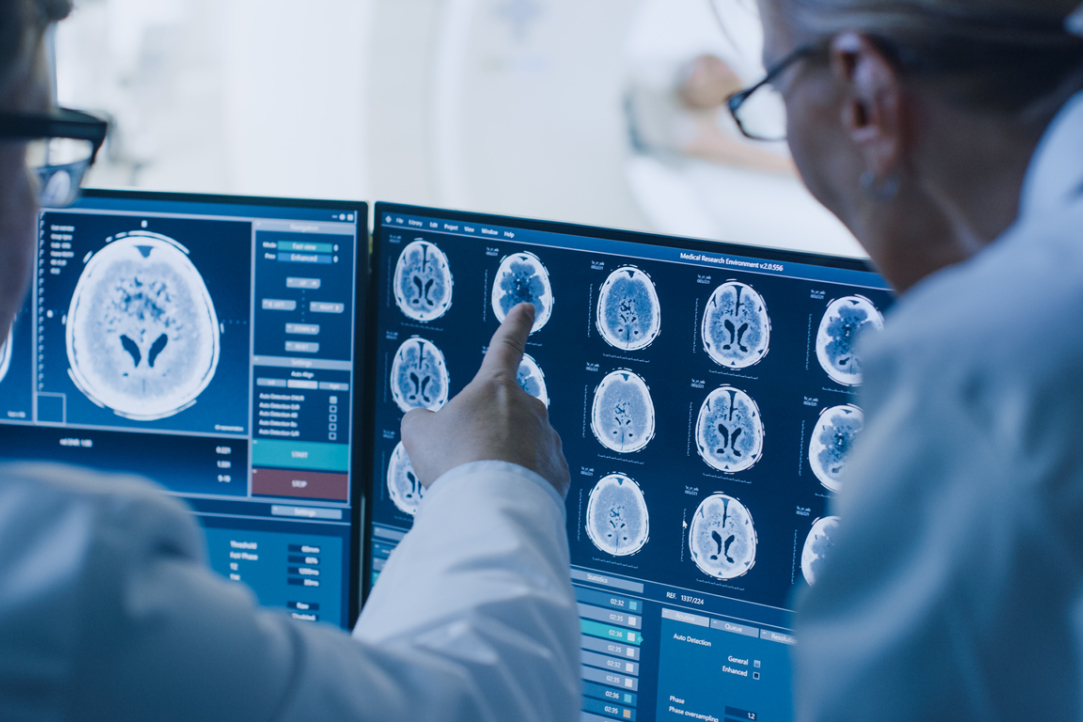
A team of researchers from Russia and Israel applied a new algorithm to classify the severity of autistic personality traits by studying subjects’ brain activity. The article ‘Brief Report: Classification of Autistic Traits According to Brain Activity Recoded by fNIRS Using ε-Complexity Coefficients’ is published in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.
When diagnosing autism and other mental disorders, physicians increasingly use neuroimaging methods in addition to traditional testing and observation. Such diagnostic methods are not only more objective, but also often reveal the presence of a disorder in cases where the doctor has insufficient behavioural data, such as when the patient is young in age.
An important task in the development of diagnostic methods is the selection of an algorithm that can identify certain brain activity patterns. Since brain cells generate many electrical impulses per second, the raw data is often insufficient to make any conclusions. The data must first be processed.
A team of researchers from Russia and Israel studied one of these algorithms. The experiment involved 26 healthy subjects, though 5 were excluded from the final sample due to noisy signals. First, the participants completed the Autism Spectrum Quotient, and based on the test result, they were divided into two groups: those with strong autistic traits and those with weak autistic traits.
Then the participants performed an interpersonal synchronized movement task: each subject was asked to move their right hand in synchronization with that of the researcher for several minutes while their brain activity was recorded. Interpersonal synchronization tasks are often used in the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders because people with ASD have difficulty coordinating joint actions.
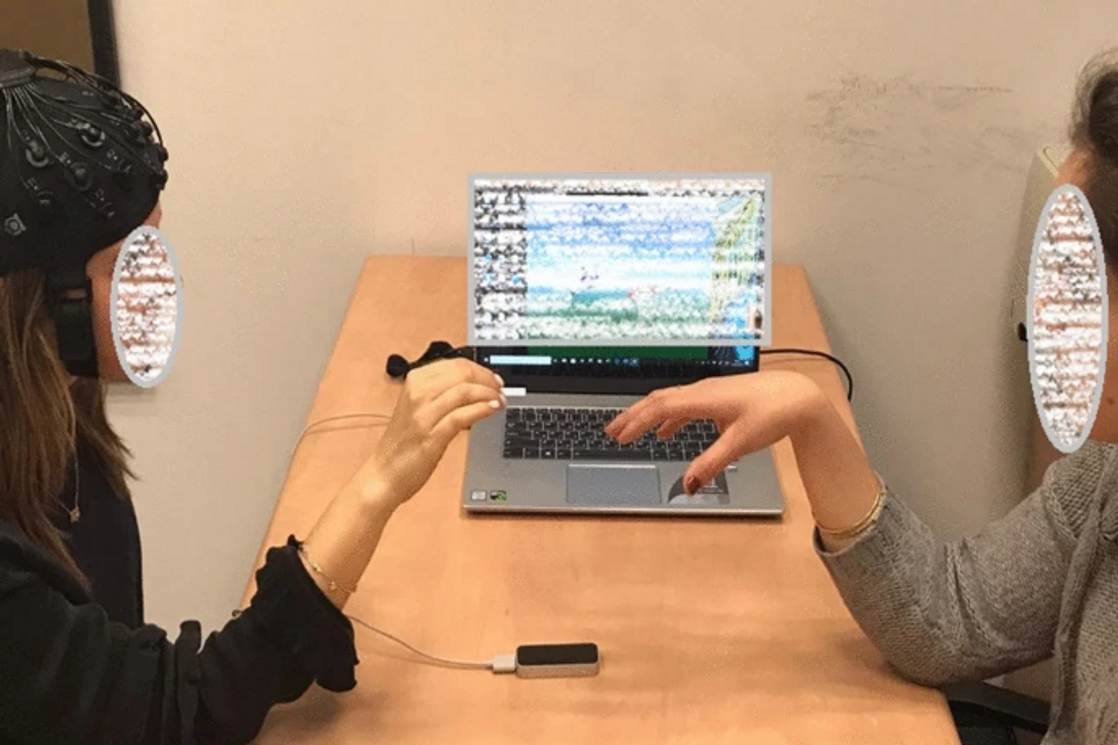

Instead of traditional MRI or EEG, the researchers chose functional near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) to record subjects’ brain activity.
FNIRS technology is based on measuring oxygen levels in the blood vessels of the brain using infrared light. Unlike fMRI, fNIRS is a more affordable and portable technology that does not make noise, so this neuroimaging technique is well suited for studying the brain activity of people with autism.
To analyse the brain activity data, the researchers used ε-complexity coefficients. This relatively new mathematical approach allowed the researchers to extract meaningful information from complex and noisy patterns. Based on the data processed in this way, the researchers used classical classification methods to divide the subjects into groups depending on the characteristics of brain activity when performing the synchronization task.
Experimenting with these algorithms, scientists were able to achieve prediction accuracy of more than 90%: in 9 out of 10 cases, the assessment of the severity of autistic traits in subjects using neuroimaging coincided with the results of the questionnaire that the participants filled out at the beginning.
The new technology can be used as a diagnostic tool for autism spectrum disorders, as it is more accessible and convenient when working with people with ASD compared to fMRI.
In addition, this study has successfully applied ε-complexity theory for the first time to decode data recorded with fNIRS. This opens up the possibility of using the new algorithm in other studies with fNIRS technology.

Yury Dubnov, Senior Lecturer at the Faculty of Computer Science
We used ε-complexity methodology, which has been developed over the past few years by Dr Boris Darkhovsky, in our study to develop an algorithm for classifying patients based on fNIRS records of brain activity. The resulting model-free technology for time series analysis can be used in cases where the prerequisites of traditional methods of analysis are violated — for example, when working with significantly non-stationary ECG and EEG signals. Therefore, this technology can be used to study other mental disorders and features, the patterns of which appear in the data.
See also:
HSE Researchers Identified the Age-Related Changes in Gamma-Band Oscillations in Auditory Cortex in Children
Researchers from the HSE Center for Language and Brain have identified previously unknown age-related changes in brain activity during the perception of auditory information in a group of children aged 7–12 years. The researchers used magnetoencephalography (MEG), an ultra-precise method of brain activity recording. The results obtained can be used to explore the impairments in language comprehension in children with autism. The study was published in the Human Brain Mapping.
HSE University Researchers Track Language Abilities of Russian Children with ASD
Researchers from the HSE Center for Language and Brain have, for the first time, described the language abilities of Russian children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) at all linguistic levels (e.g., phonology, lexicon, morphosyntax, and discourse), using a language test that takes into account the psycholinguistic variables most relevant for Russians. The study was published in Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.
Complex Phonological Tests Are Useful for Diagnosing Reading Dysfunction
HSE University researchers have confirmed that the level of phonological processing skills in children can impact their ability to master reading. Complex phonological tests are best suited to detect phonological impairment. The study was published on September 6, 2020, in the Journal of Research in Reading.