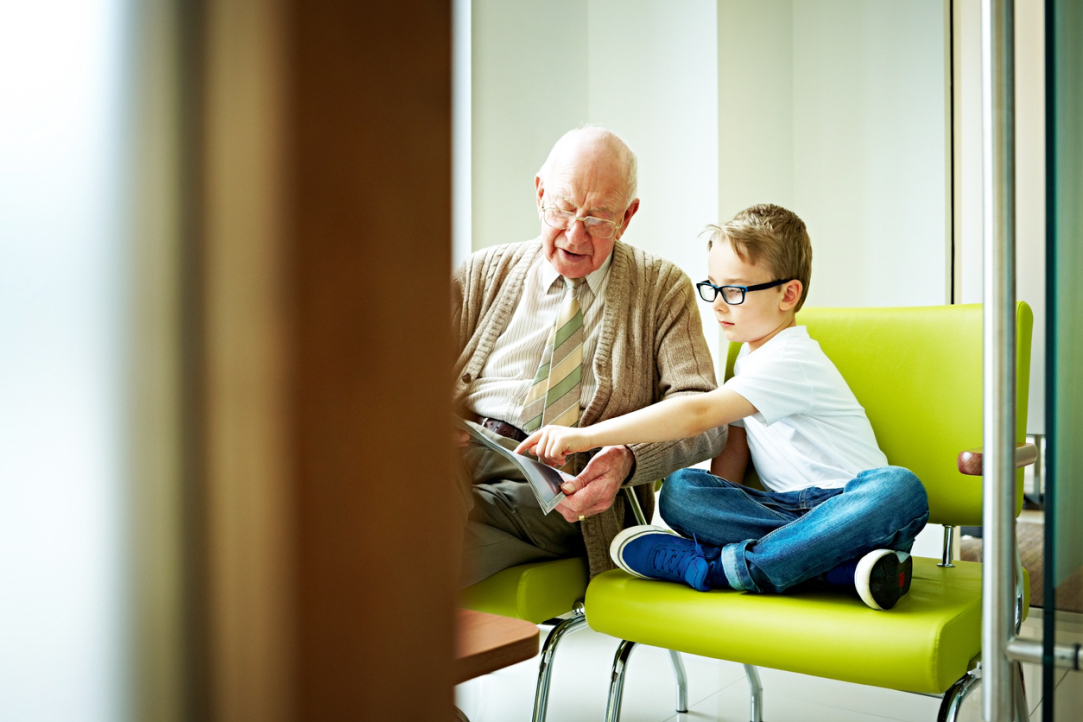
Researchers Investigate Why Older People Read More Slowly
One of the most obvious changes that comes with ageing is that people start doing things more slowly. Numerous studies have shown that ageing also affects language processing. Even neurologically healthy people speak, retrieve words and read more slowly as they get older. But is this slowdown inevitable? Researchers from the Higher School of Economics have been working to answer this question in their article ‘No evidence for strategic nature of age-related slowing in sentence processing’.
Researchers Discover Brain Cortex Activity Differences in Children with Arthrogryposis
Researchers from the Higher School of Economics and the Turner Scientific and Research Institute for Children’s Orthopedics have discovered that in children with arthrogryposis, the power of electrical activity in the brain cortex decreases, while its dynamics remains the same as in healthy children. The results of the study were published in the paper ‘Characteristics of electrophysiological activity of the cerebral cortex in children with arthrogryposis’.
Alzheimer, Parkinson Et Al
Globally, the burden of neurological disorders (Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, epilepsy etc) has increased substantially over the past 25 years. This problem is the topic of a recent report by the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) international project, which was published in The Lancet. One of its participants is Vasily Vlassov, Professor at the HSE Faculty of Social Sciences.
Researchers Learn More about Maximizing Brain Use
Neuroscientists from Higher School of Economics and Charité University Clinic in Berlin have come up with a new multivariate method for predicting behavioural response to a stimulus using information about the phase of preceding neuronal oscillations recorded with EEG. The method may eventually find practical application in fields such as competitive sports, education and patient treatment. The study's findings are published in the paper ‘On optimal spatial filtering for the detection of phase coupling in multivariate neural recordings’.